


WordPress is undoubtedly the most popular content management system (CMS) for creating websites today. A CMS lets users build, manage, and modify the content of websites through a user-friendly graphical interface.
WordPress is popular because it is a feature-rich tool that lets users build a custom website without having to code one from scratch. Nearly half of all websites – 42.5%, to be exact – are built on WordPress.
This all-in-one beginner’s guide will show you how to create a WordPress website. You will learn about the difference between WordPress.org and WordPress.com and whether WordPress is the best fit for your project.
Furthermore, this guide will provide step-by-step WordPress tutorials and detailed instructions on the installation process, content creation, and maintenance.
When you look up “WordPress” on a search engine, you will notice there are two types of WordPress available – WordPress.org and WordPress.com. It’s important to know that these two platforms are significantly different.
In brief, WordPress.org is the website where you can download the CMS software and use it to build and manage the website. The platform is open-source, so anyone can access it for free and modify it to their liking at no additional cost.
A major benefit of WordPress is its customizability. Users can add extensions called ‘plugins’ to the software to enable custom features, from eCommerce, speed optimization, to website analytics.
To install WordPress, you must purchase web hosting. It’s the service responsible for storing your site’s data and making it available to the worldwide web.
Fortunately, you can find hosting providers that offer reliable service at an affordable price, ranging from $2/month to $10/month. WordPress hosting plans are specifically optimized for WordPress, offering the best performance and security.
On the other hand, WordPress.com is a website builder that runs a custom version of the open-source WordPress CMS software. It is a hosted platform – meaning all websites created on WordPress.com will be hosted or stored on their proprietary servers.
To start a website on WordPress.com, all you need to do is go to the website, create an account, and choose a plan. Which one you pick will determine the features and flexibility you can access on the website builder.
For example, the Free plan doesn’t allow users to use a custom domain. To do so, you must at least upgrade to the Personal plan. Additionally, eCommerce features can only be unlocked by upgrading to the top-tier plan.
The table below illustrates the differences between WordPress.org vs.WordPress.com further:
| WordPress.org | WordPress.com (Free Plan) | WordPress.com (Paid Plans) | |
| Pricing | Free | Free | Personal: $4/month; Premium: $14/month; Business: $33/month; eCommerce: $59/month |
| Custom domain | Yes | No | Yes |
| Storage space | Depends on the web hosting plan | 3 GB | Personal: 6 GB; Premium: 13 GB; Business: 200 GB; eCommerce: 200 GB |
| Remove ads | Yes | No | Yes |
| Advanced design customization | Yes | No | Personal: LimitedPremium, Business, eCommerce: Yes |
| Membership site | Yes | No | Yes |
| Google Analytics integration | Yes | No | Personal: NoPremium, Business, eCommerce: Yes |
| Search Engine Optimization (SEO) tools | Yes | No | Personal, Premium: NoBusiness, eCommerce: Yes |
| Install custom plugins | Yes | No | Personal, Premium: NoBusiness, eCommerce: Yes |
| Upload themes | Yes | No | Personal, Premium: NoBusiness, eCommerce: Yes |
| SFTP and database access | Yes | No | Personal, Premium: NoBusiness, eCommerce: Yes |
| eCommerce features | Yes | No | Personal, Premium, Business: No, eCommerce: Yes |
| Support | Through hosting provider | No | Yes |
WordPress.org is much more versatile to use compared to WordPress.com. Whether you want to create a small or complex website with lots of content, WordPress.org is an excellent choice.
As long as your hosting has sufficient resources, WordPress.org will be able to run your website smoothly. Thankfully, most web hosting companies let you upgrade your hosting plan with ease.
In contrast, WordPress.com is best suited for simple or small websites. If there’s a need to set up a website quickly, WordPress.com can also be a better fit.
However, it’s not recommended for users who want to have a fully customizable website with plans to scale in the future. The limitations imposed on most WordPress.com plans make it difficult to take complete control of a website.
With that in mind, this tutorial will focus on WordPress.org, as there’s a lot more you can do with it than with WordPress.com.
As mentioned above, installing WordPress requires a web hosting service. There are many hosting providers to choose from, though my personal recommendation is Hostinger.
Their hosting service performed well in my 90-day tests, having only 1 minute of downtime. The price also offers great value for money – the WordPress hosting plans start from $1.99/month to $11.59/month.
Alternatively, check out NameHero, LiquidWeb, and KnownHost. Each of them offers fast-performing hosting services at affordable prices as well.
Once you’ve purchased a hosting plan, you can initiate installation. All the hosting providers mentioned above include an auto-installer. This makes it possible to set up WordPress right from your hosting account, so there’s no need to download the software package yourself.
The automatic installation is more or less the same on all hosting platforms. For illustration purposes, I will show you how to install WordPress on Hostinger’s control panel.
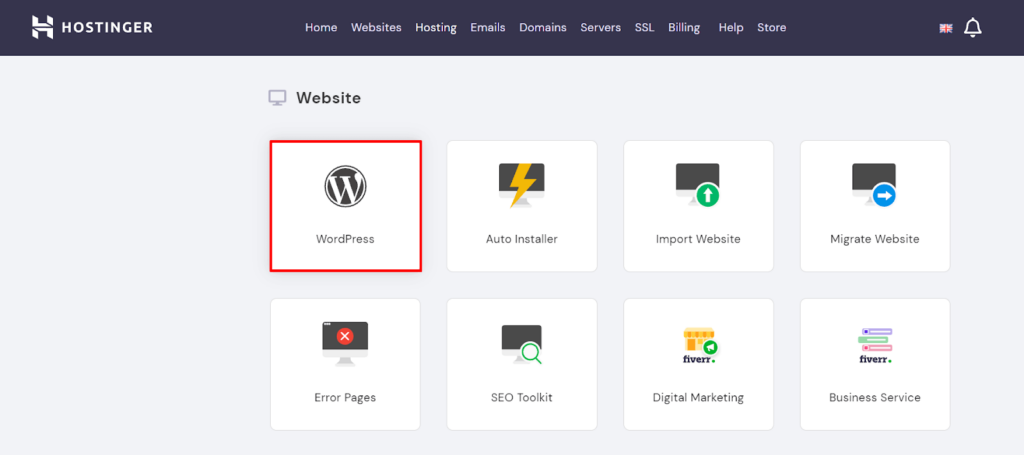
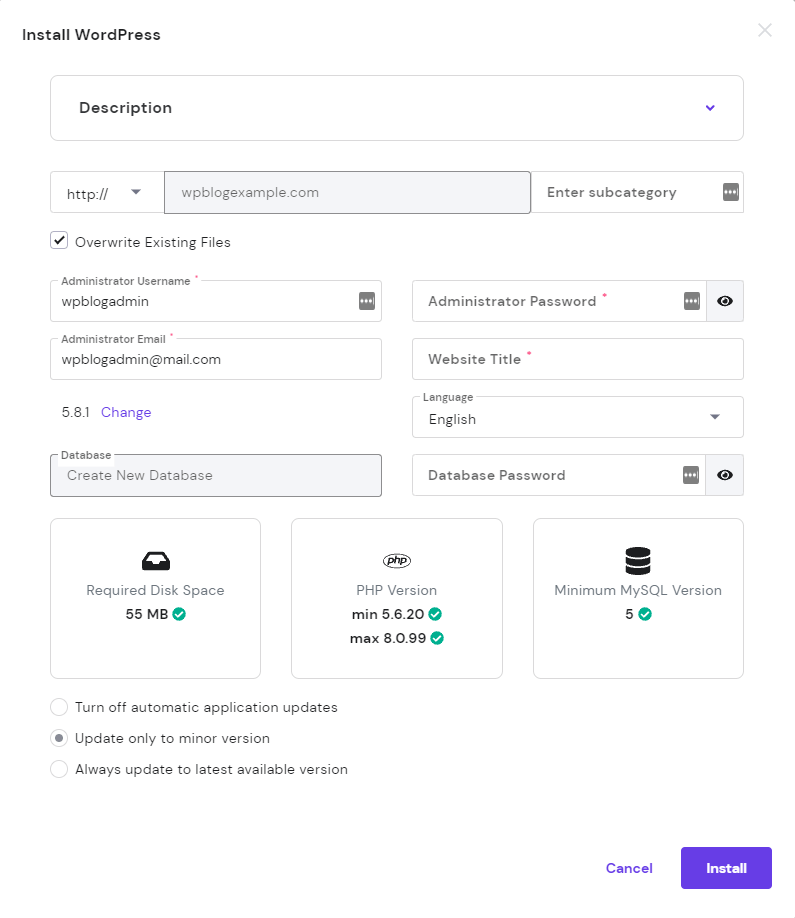
If the auto-installer doesn’t work, it’s also possible to install WordPress manually using an FTP client. The process may take longer as it involves some technical knowledge, so make sure to follow the instructions carefully.
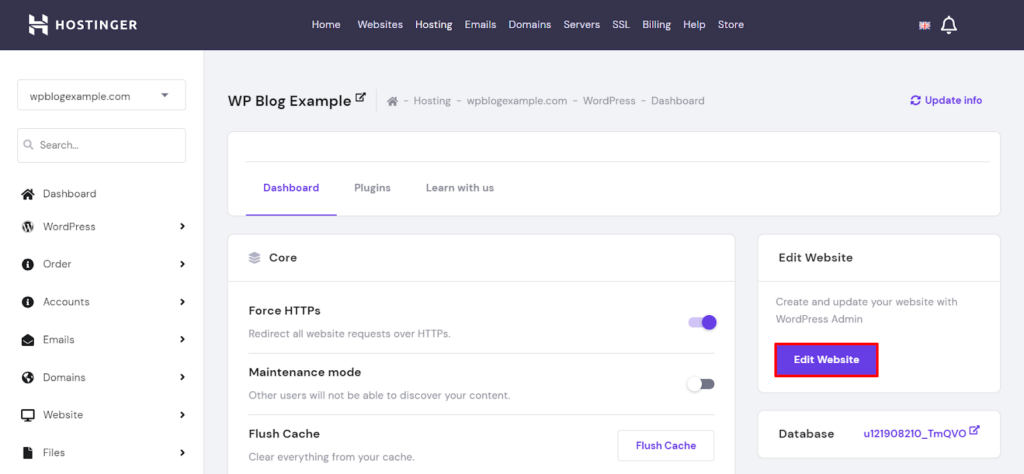
The WordPress admin dashboard is where you’ll be able to make changes to your website.
Most hosting providers offer a button to sign in to the admin dashboard from their control panel. However, it’s also possible to access the dashboard directly by following these instructions:
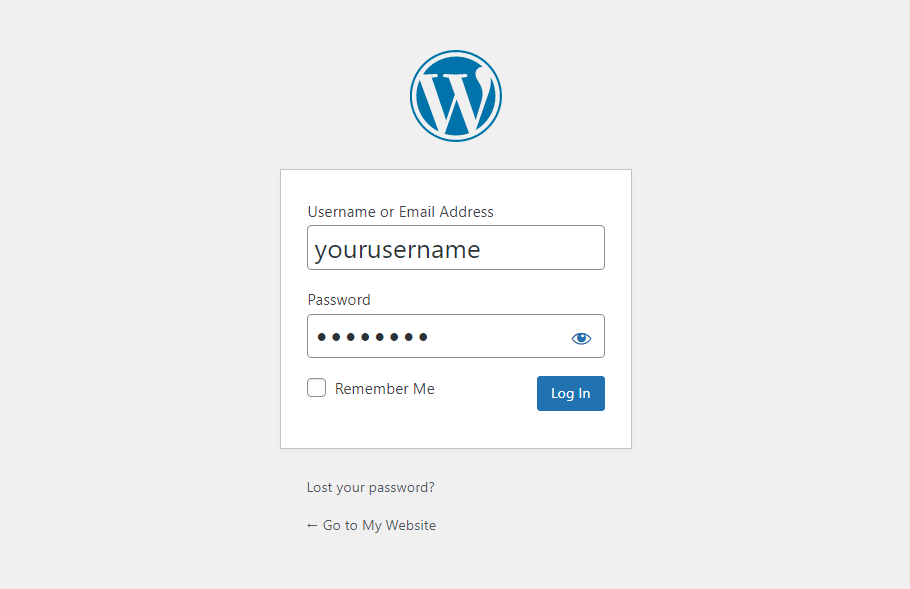
Unfortunately, hacker attacks are prevalent for WordPress sites. It’s essential to keep the admin dashboard of your WordPress site secure from unauthorized access. Fortunately, there are simple ways to do so:
Let’s explore the WordPress admin dashboard and its settings. This is where you can make changes to your site.
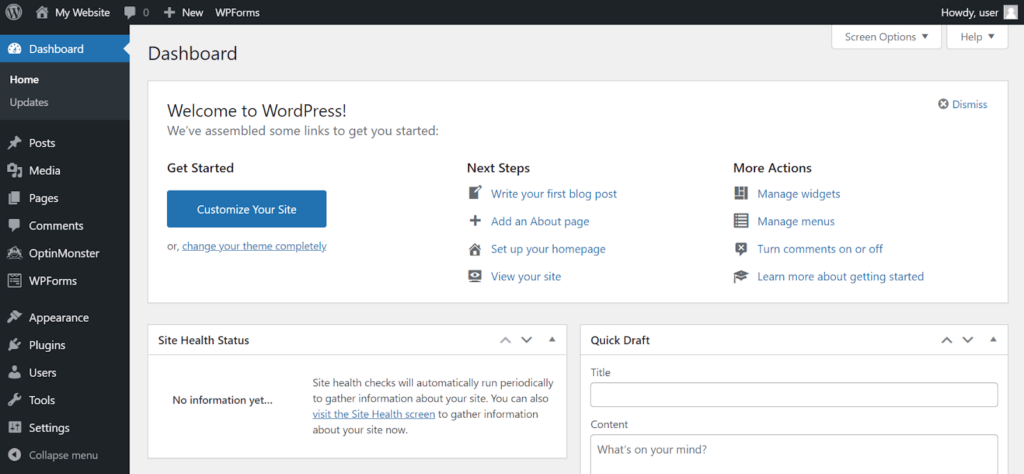
Here’s a quick overview of every menu item you’ll find in the sidebar:
In the following sections, I will explain in detail some basic tasks you can do in the admin dashboard.
A WordPress theme is a pre-made design template for a WordPress site. By activating one, you’ll be able to instantly change the look of a site without having to edit the code. Many WordPress themes let you customize it further to make it truly unique.
Free and premium WordPress themes are available via the official directory and third-party sources such as ThemeForest and TemplateMonster. Free WordPress themes are generally more limited in features compared to premium ones.
Some themes are specifically designed for particular use cases, such as portfolio, blog, business, or eCommerce. For the best result, make sure to choose a premium or free theme that fits the purpose of your WordPress website. Here are some recommendations:
To install a new theme, log in to the WordPress admin area, then:
To install a theme from the WordPress directory, browse until you find the one you like most. Select Preview to see how it’ll look on your WordPress site.
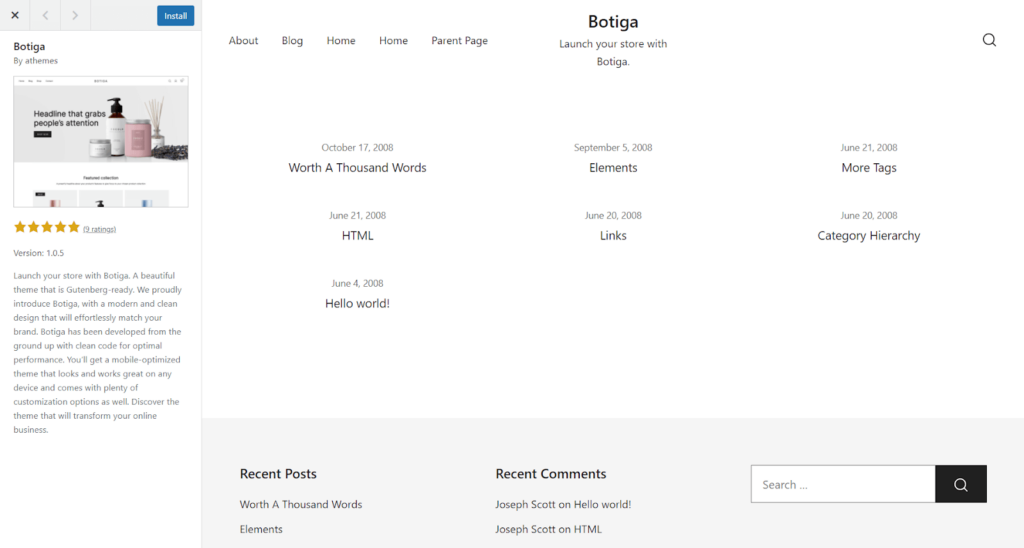
If you’re happy with it, select Install, then Activate.
To upload a WordPress theme from a third-party source, make sure that you have downloaded the theme file first.
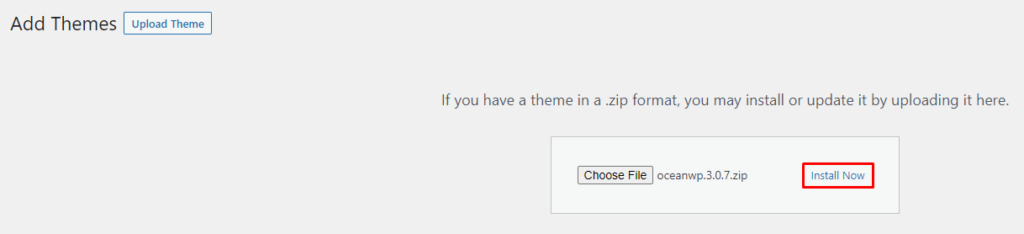
WordPress plugins add additional features to WordPress, extending its functionality. They can be easily installed, updated, and removed without having to edit the website’s code.
Like themes, there are free and premium WordPress plugins to choose from. There are also freemium ones – premium plugins with limited features that can be installed for free. Although many free plugins are sufficient, some users might benefit from the extra features offered by premium ones.
Take a look at some of these essential WordPress plugins:
To install a new plugin, log in to the WordPress admin area, then:
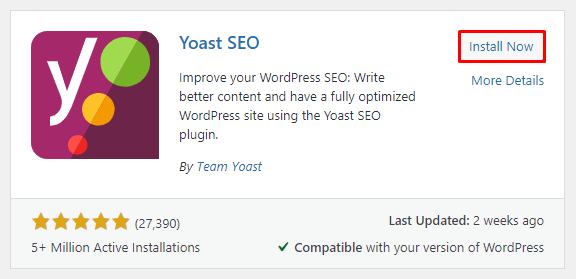
A page contains content that often stays the same for a long time, such as the About and Contact pages.
To add a new page, log in to the WordPress dashboard and go to Pages -> Add New. You will be taken to the block editor, where you can add and manage content on the new page.

A piece of content is called a block. It can be a paragraph, an image, a video, a form, or other types of content. Each block can be added, rearranged, edited, and deleted easily.
To add the main title, simply type it into the designated Add title section.
To add the body text, type it into the block under the title. Alternatively, you can add other types of content by clicking the “plus” button to open the block library.
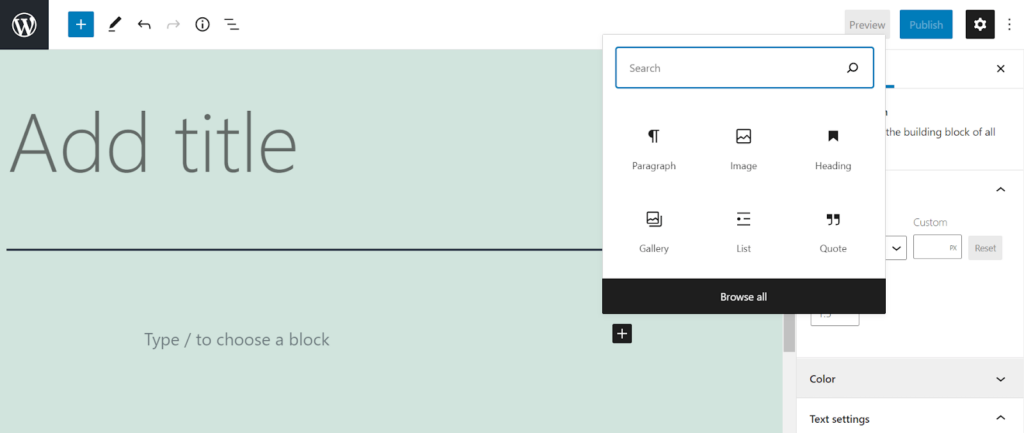
To find the block you want, browse them one by one or use the search bar. There are six categories of blocks – Text, Media, Design, Widgets, Theme, and Embeds. Although they are sufficient for most websites, you can get more block types by installing certain WordPress plugins.
Once you’re done adding content to the page, make sure to apply the correct settings before publishing it. Click on the “gear” icon on the top right of the editor to find the page settings:
Once you’re done with the settings, feel free to Preview the page and click the Publish button. However, if you want to publish the page at a later time, select Save draft.
A post or a blog post usually contains timely content. Unlike pages, posts tend to be regularly updated.
Fortunately, the process of publishing pages and posts are very similar. Both use the block editor, with the only difference being the options in the post settings. For example, instead of being organized by parent and child pages, WordPress posts use categories and tags.
To create a post, log in to the admin dashboard and navigate to Posts -> Add New.
In the Add title section, enter the text for the main title of the post. Then, begin to add paragraphs and other types of content into blocks. Click “plus” to open the block library and input the content you want.
Once you have finished adding content, select the “gear” icon in the top right corner to expand the post settings.
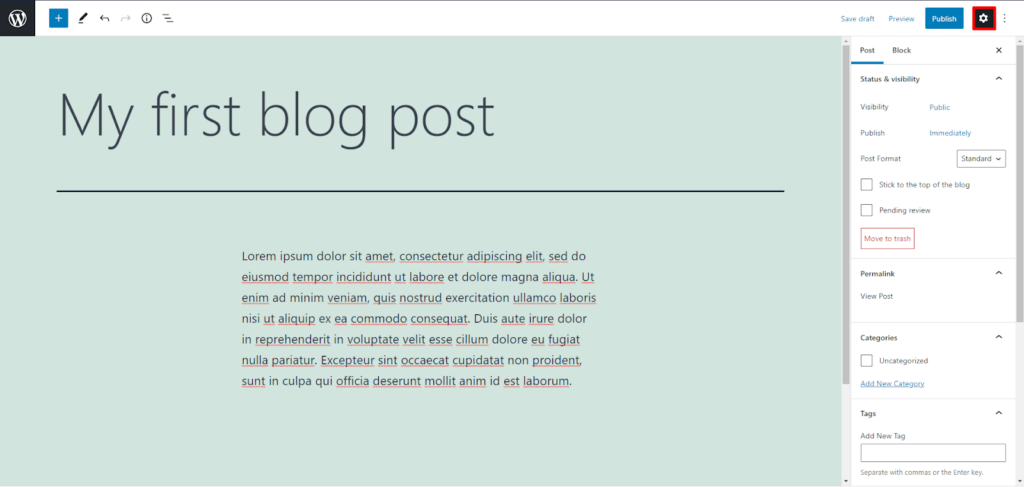
After setting up the status and visibility, permalink, and a featured image, assign categories and tags to the post.
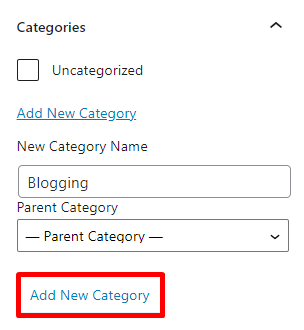
To assign categories to a post, simply check the box next to the category name. If there’s no category yet or you want to add more, select Add New Category.
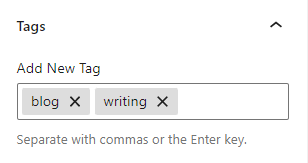
To add tags, enter the words or phrases into the field, separated by commas.
Make sure that your content is ready and the settings are correct before you hit Publish.
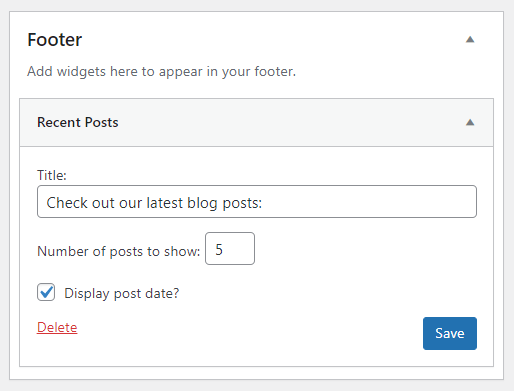
A widget is a block of content that you can add to certain areas of your WordPress site, such as the sidebar, header, and footer.
Let’s go over some of the essential widgets to add to a WordPress website:
As of WordPress 5.8, widgets are part of blocks. So, in addition to the legacy options mentioned above, users can add any item from the block library as a widget.
This new block-based widget system is great for WordPress users who are already familiar with the block editor. However, if you prefer to separate widgets from the block system, an official WordPress plugin lets you use the classic widget editor.
Here’s how to add a widget using the block-based widget editor:
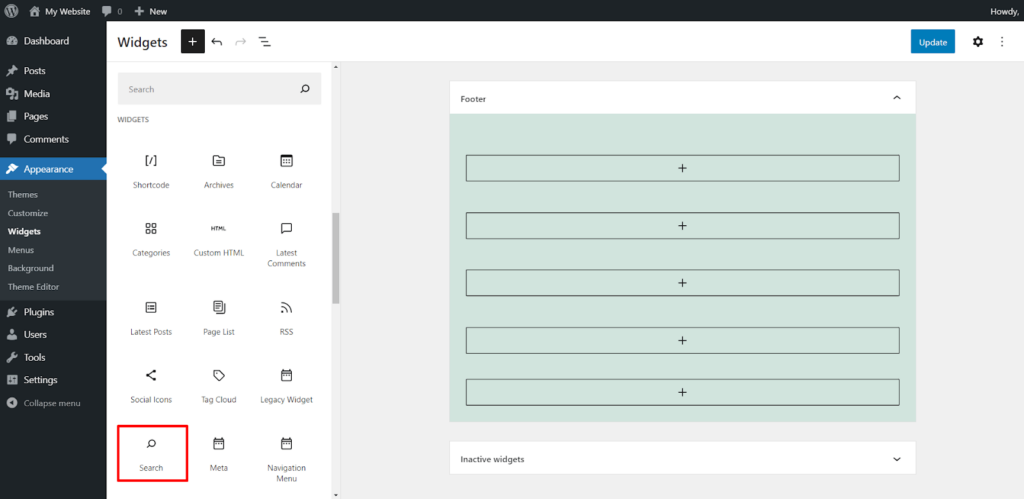
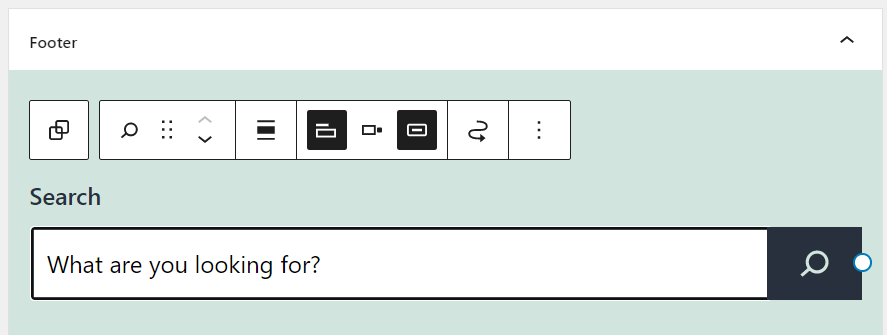
Alternatively, here’s how to add a widget using the classic editor:
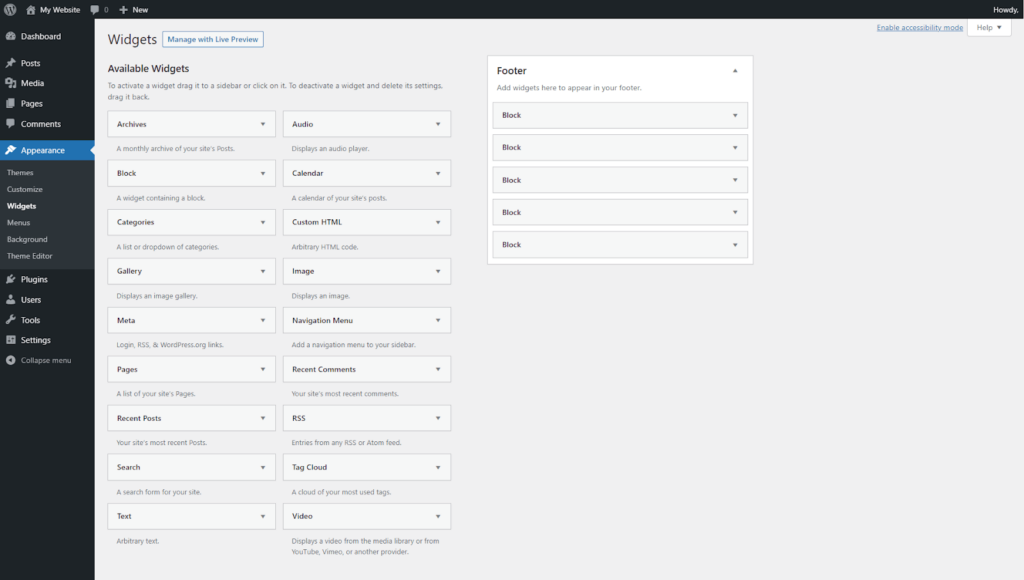
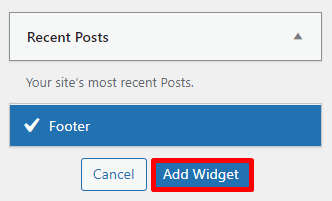
A menu is essential for helping users navigate a WordPress website and find the content they’re looking for. Without a menu, the user experience of a site might become frustrating, causing users to leave the site.
Before I begin, decide whether you want to display blog posts on the Home page or a separate Blog page. If it’s the former, feel free to skip these steps:
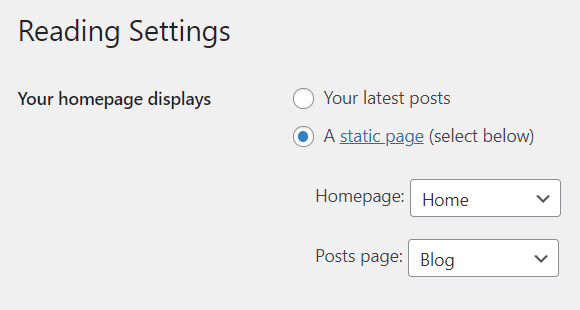
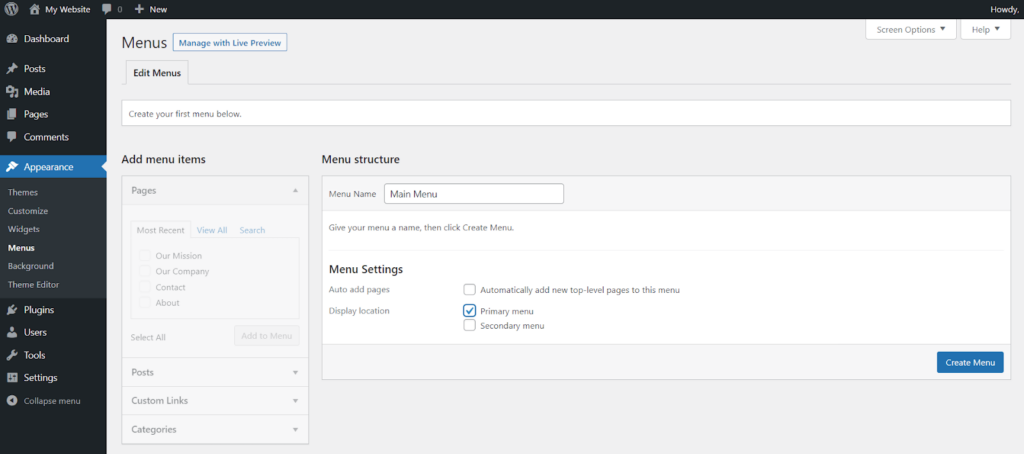
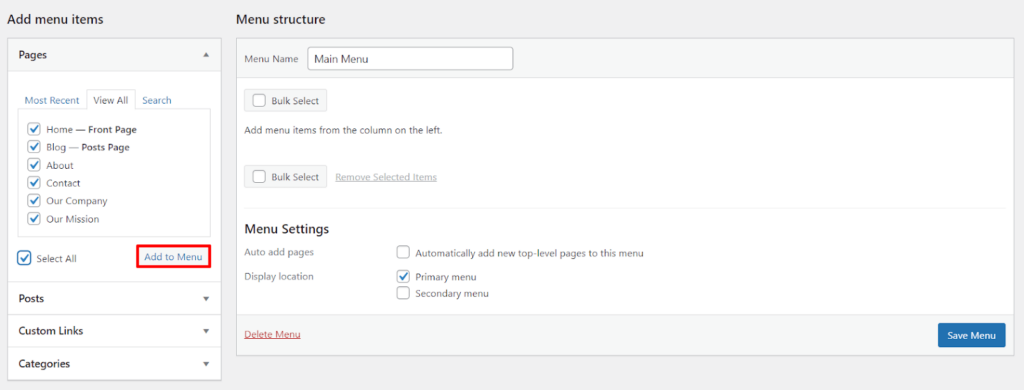
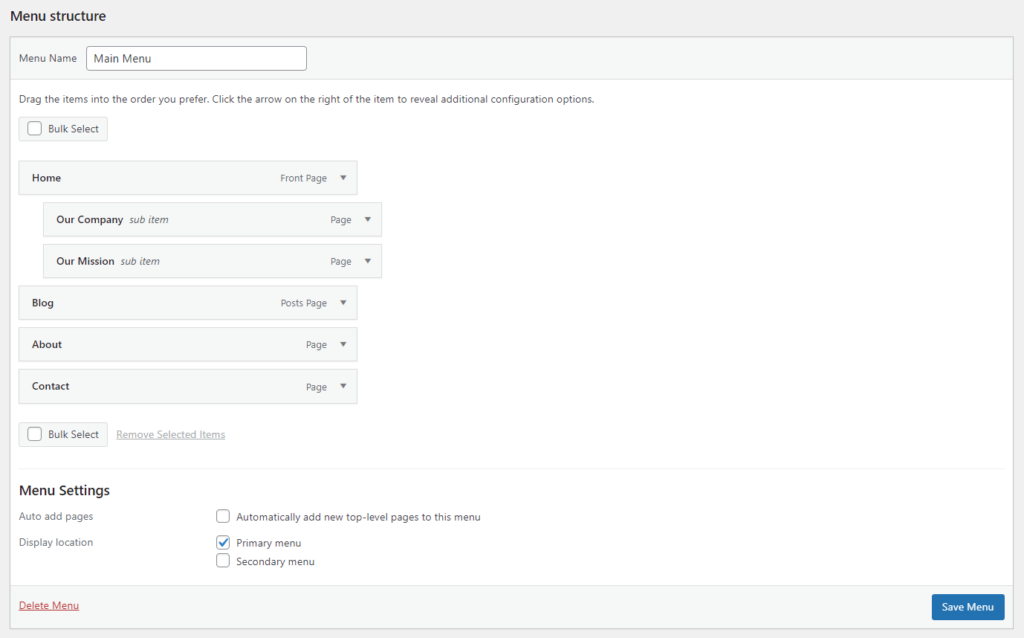
Now, let’s create the navigation menu:
Updating the WordPress software, theme, and plugins is very important, especially for security. Outdated software can have vulnerabilities that let hackers access your site. This can be a serious threat to the data privacy and system security of a website.
The secondary benefit of updating WordPress is unlocking new features. By keeping up with the latest version of WordPress, you’ll access new ways to take your WordPress site to the next level.
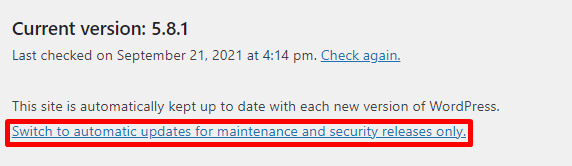
Thankfully, since WordPress 5.6, users can set up automatic background updates for WordPress core, plugins, themes, and translation files.
To opt for automatic core updates:
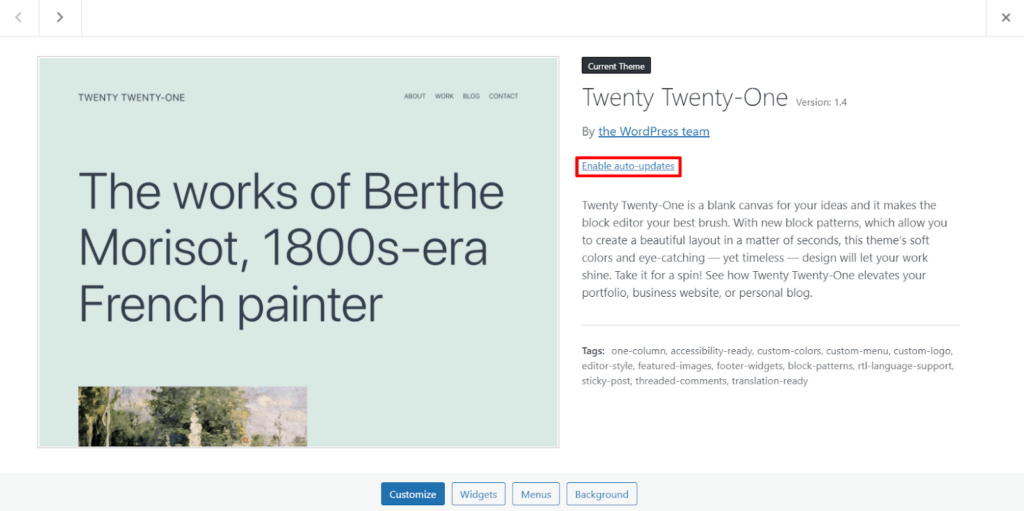
To set up automatic updates for a WordPress theme:
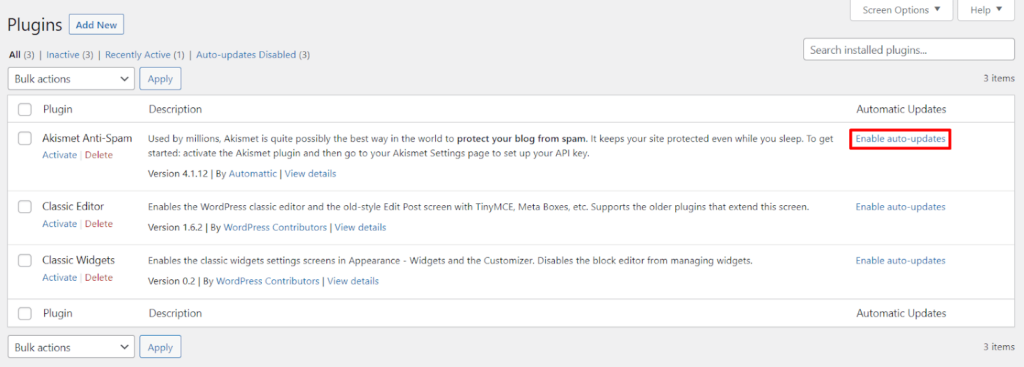
To automatically update plugins:
If you choose to manually update WordPress, regularly checking Dashboard -> Updates is highly recommended. If there’s an update for core, plugins, or themes, you will see a notification for it.
Having backups of your WordPress site is very important in case of a situation such as a hacker attack or accidentally deleted data. You’ll be able to restore your site using the backup and get it to work normally again.
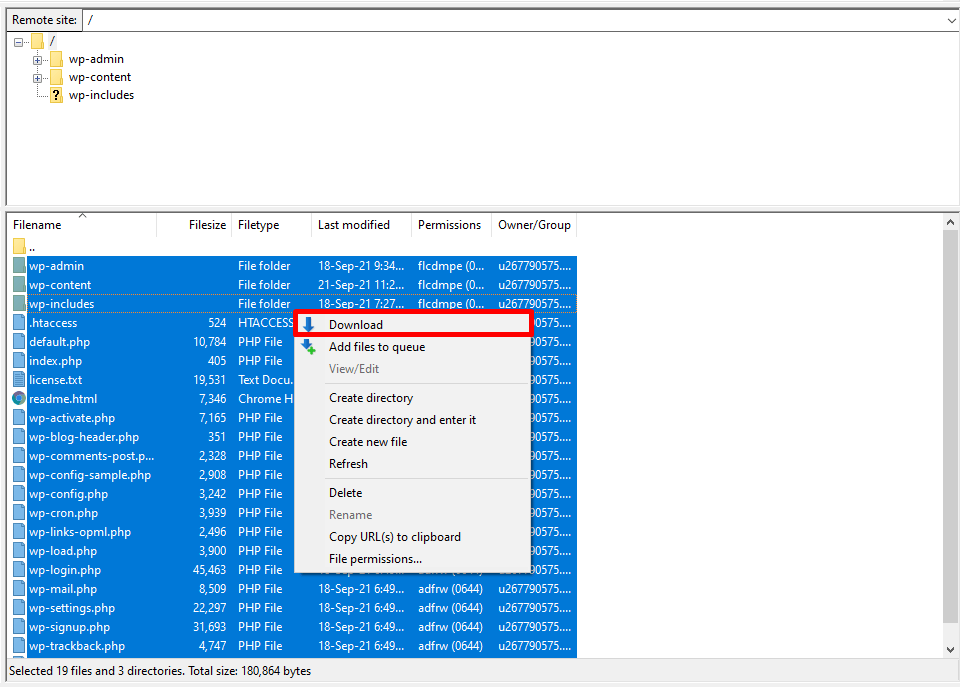
First, let’s explore how to backup WordPress manually via an FTP client:
Second, let’s explore how to backup WordPress automatically using a plugin. There are many backup plugins, but as an example, I’ll use UpdraftPlus:

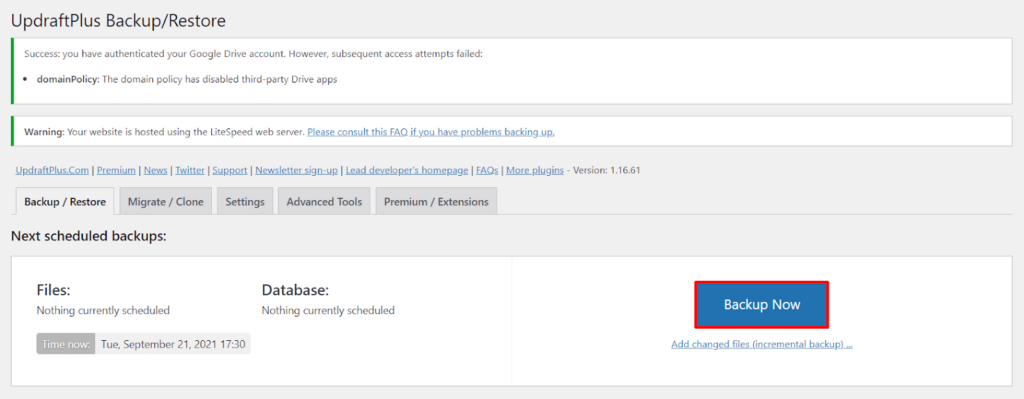
Check the settings you want to use, and proceed to Backup Now.
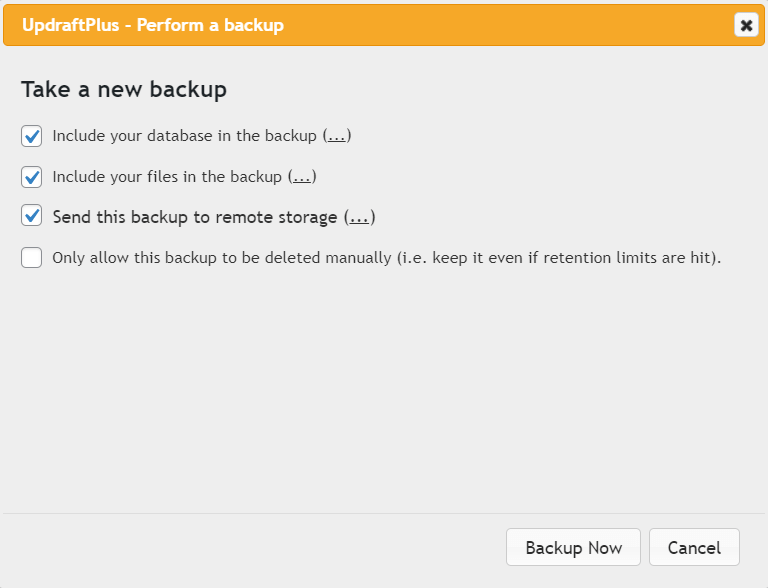
On the Files backup schedule and Database backup schedule drop-down menus, select how often you want the plugin to perform a backup.
You can also choose how many backups to retain. If you select two, then the third latest backup and older will automatically be deleted.
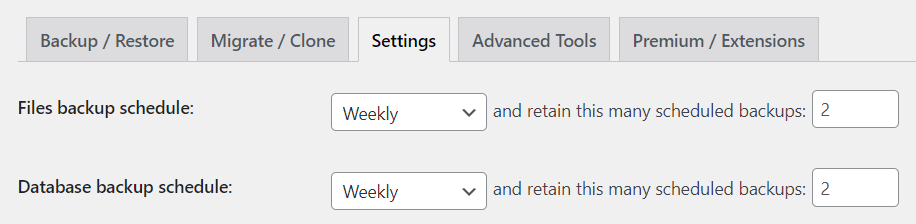
Click Save Changes.
WordPress is a feature-rich, scalable, and beginner-friendly platform for creating any website. In this all-in-one WordPress tutorial, you can find everything you need to know to get started, including:
I hope that this guide helped you learn all about WordPress and how to create a new website for your personal or business needs.
To get more in-depth knowledge on other WordPress topics, take a look at these advanced WordPress tutorials and best-of lists:
Check out the complete list of WordPress resources to get recommendations on the best WordPress page builders, plugins, and hosting.